Eye Transplant Cost in India
When people refer to an “eye transplant,” they often imagine a full eyeball replacement. However, a complete eye transplant is currently not possible due to the complexity of the optic nerve, which cannot be reconnected to the brain. In medical terms, an eye transplant usually refers to a corneal transplant, also known as keratoplasty.
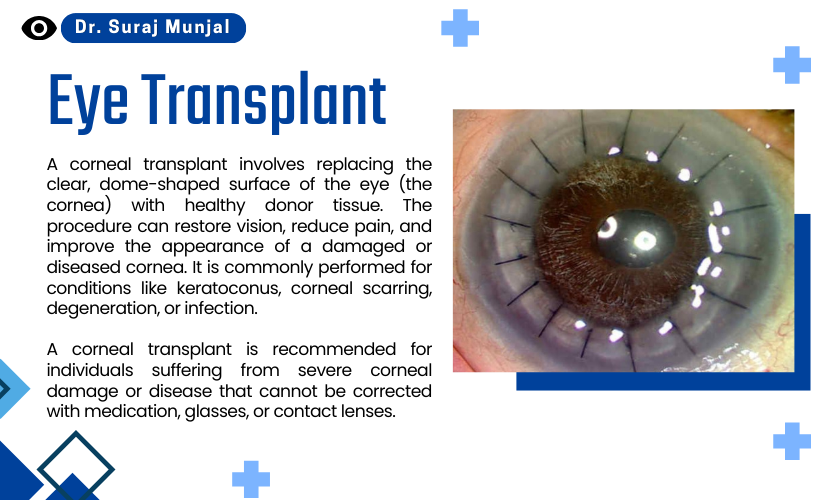
A corneal transplant involves replacing the clear, dome-shaped surface of the eye (the cornea) with healthy donor tissue. The procedure can restore vision, reduce pain, and improve the appearance of a damaged or diseased cornea. It is commonly performed for conditions like keratoconus, corneal scarring, degeneration, or infection.
In India, the cost of a corneal transplant is remarkably affordable compared to many other countries. On average, the cost of an eye transplant in India ranges from ₹50,000 to ₹2,50,000, which is approximately $600 to $2,900, depending on the type of transplant, surgeon, and hospital.
Despite its low price, India offers world-class ophthalmic care, access to certified eye banks, and internationally trained surgeons, making it a top destination for international patients seeking affordable yet high-quality eye surgery.
If you're experiencing severe vision loss due to corneal disease, undergoing a corneal transplant in India could be a safe, cost-effective, and life-changing decision.
Table of Contents
Who Needs an Eye Transplant?
A corneal transplant is recommended for individuals suffering from severe corneal damage or disease that cannot be corrected with medication, glasses, or contact lenses. The cornea, which is the clear front surface of the eye, plays a vital role in focusing light and maintaining clear vision. When it becomes cloudy, scarred, swollen, or misshapen, vision can become blurry, distorted, or even completely lost.
In such cases, a healthy donor cornea can replace the damaged one, restoring visual clarity and relieving discomfort or cosmetic abnormalities.
Common Conditions That Require a Corneal Transplant:
- Keratoconus: A progressive eye disorder where the cornea thins and bulges into a cone shape, distorting vision. In advanced stages, corneal transplant is often the only solution.
- Corneal Scarring: Scars from injury, infection, or previous eye surgeries can cause permanent opacity in the cornea, obstructing light from entering the eye correctly.
- Fuchs’ Endothelial Dystrophy: A genetic condition where the innermost corneal layer (endothelium) deteriorates, leading to swelling, blurriness, and visual impairment.
- Infectious Keratitis: Severe bacterial, fungal, or viral corneal infections that damage the tissue may require transplantation if medical treatment fails.
- Corneal Degeneration or Dystrophies: These include inherited disorders where the cornea gradually loses its transparency or develops deposits, leading to vision loss over time.
- Failed Previous Corneal Graft: If a patient has already undergone a corneal transplant and the graft fails, a repeat procedure may be necessary.
- Chemical or Thermal Burns: Severe burns from chemicals or heat can destroy corneal tissue, leaving transplantation as the only viable option for sight restoration.
Patients with these conditions may experience symptoms such as blurred or cloudy vision, increased sensitivity to light, eye pain, or visible corneal opacity. When these symptoms interfere with daily life and other treatments are ineffective, a corneal transplant becomes the most effective way to restore vision and quality of life.
What are the Different Types of Eye (Corneal) Transplants Performed in India?
India offers a wide range of corneal transplant techniques tailored to the patient’s specific condition. The type of eye transplant recommended depends on the location and depth of the corneal damage. Indian eye surgeons are highly skilled in performing both traditional and advanced forms of keratoplasty using donor tissue from certified eye banks.
Penetrating Keratoplasty (PK) – Full-Thickness Corneal Transplant
It is the most traditional type of corneal transplant, where the entire thickness of the damaged cornea is removed and replaced with healthy donor tissue. It is commonly used for conditions like deep scarring, severe keratoconus, or advanced dystrophies. PK offers excellent long-term outcomes, though healing takes several months.
Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty (DALK)
In DALK, only the front layers of the cornea are replaced, preserving the patient’s healthy inner endothelial layer. The procedure is ideal for keratoconus and surface scarring, and it reduces the risk of graft rejection because the endothelium is not replaced. Recovery is faster and more predictable compared to full-thickness transplants.
Descemet’s Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty (DSEK/DSAEK)
It involves replacing the innermost layer of the cornea (the endothelium), which is responsible for maintaining corneal clarity. DSEK or DSAEK is commonly used in conditions like Fuchs’ endothelial dystrophy or pseudophakic bullous keratopathy. It allows for smaller incisions, faster visual recovery, and a lower risk of complications.
Descemet Membrane Endothelial Keratoplasty (DMEK)
An ultra-precise form of endothelial transplant, DMEK involves transplanting only the Descemet’s membrane and endothelial cells, making it thinner and more delicate than DSEK. It offers superior visual outcomes and minimal rejection rates, but it requires a highly skilled surgeon due to its technical complexity.
Artificial Cornea Transplant (Keratoprosthesis – KPro)
In rare and severe cases where conventional grafts have failed or are not viable (e.g., due to repeated rejections), a synthetic or artificial cornea may be implanted. Known as Boston KPro, this option is typically a last resort and is performed in select specialised centres in India.
What is the Cost of an Eye Transplant in India?
The cost of an eye transplant in India, specifically a corneal transplant, typically ranges between ₹50,000 and ₹2,50,000 (approximately $600 to $2,900). It includes the surgical procedure, donor corneal tissue, and associated medical services. The pricing can vary depending on the type of transplant performed, the reputation of the hospital, and the surgeon’s expertise.
For a full-thickness corneal transplant (Penetrating Keratoplasty), the cost usually falls within ₹60,000 to ₹1,50,000. For more advanced and technically demanding procedures like DSEK or DMEK, the price may go up to ₹1,20,000 or even ₹2,50,000, especially in major eye care centres or multi-speciality hospitals.
Government hospitals or charitable eye institutes may offer subsidised rates starting from ₹30,000 to ₹40,000, but waiting times are longer and services may be limited to domestic patients.
Most private hospitals and internationally accredited eye centres offer all-inclusive packages, which generally cover:
- Donor cornea from a certified eye bank
- Surgical procedure charges
- Surgeon and OT fees
- Standard hospital stay (if required)
- Routine post-operative medications and check-ups
India remains one of the most cost-effective countries in the world for corneal transplantation, offering high-quality surgery at one-fifth the cost of similar procedures in the West. Patients receive access to modern technology, skilled corneal specialists, and seamless care at a transparent and affordable price.
Cost Breakdown of Eye (Corneal) Transplant in India
The total cost of a corneal transplant in India ranges between ₹50,000 and ₹2,50,000 for one eye. This amount includes several essential components.
- First, patients undergo pre-operative diagnostic tests, which typically cost between ₹3,000 and ₹6,000. These tests include corneal topography, blood work, and detailed vision assessments to confirm eligibility and choose the appropriate surgical approach.
- The donor cornea, sourced from a certified eye bank, adds ₹10,000 to ₹30,000 to the total cost depending on availability, preservation method, and whether it’s obtained from a public or private source.
- The surgical fee itself usually falls between ₹35,000 and ₹85,000, depending on whether the patient requires a standard full-thickness transplant (PK) or a more advanced procedure like DSEK, DMEK, or artificial cornea implantation.
- Charges for hospital resources, including use of the operation theatre, surgical tools, and nursing care, range from ₹5,000 to ₹15,000.
- Post-operatively, patients will need eye drops, steroid medications, and antibiotics, which are usually priced between ₹2,000 and ₹5,000 for the initial recovery phase.
- Additionally, hospitals often schedule two to three follow-up visits, with total consultation costs amounting to ₹1,000 to ₹3,000.
|
Component |
Estimated Cost (INR) |
Details |
|
Pre-operative Eye Evaluation |
₹3,000 – ₹6,000 |
Includes corneal imaging, vision tests, and blood work |
|
Donor Cornea from Eye Bank |
₹10,000 – ₹30,000 |
Eye bank fee for screened, preserved donor tissue |
|
Corneal Transplant Procedure |
₹35,000 – ₹85,000 |
Surgical fee depending on the type (PK, DSEK, DMEK, etc.) |
|
Operating Theatre & Hospital Use |
₹5,000 – ₹15,000 |
OT charges, hospital equipment, and nursing staff |
|
Post-operative Medications |
₹2,000 – ₹5,000 |
Antibiotics, steroids, and lubricants |
|
Follow-up Consultations |
₹1,000 – ₹3,000 |
Typically, 2–3 visits are included in most packages |
|
Total Estimated Cost |
₹50,000 – ₹2,50,000 |
Complete cost for one eye, including standard recovery |
Together, these components contribute to the all-inclusive cost of the surgery, which is significantly lower in India compared to most developed countries.
Eye (Corneal) Transplant Cost Comparison with Other Countries
India has become a global hub for affordable and high-quality eye surgeries, especially corneal transplants. Patients from the United States, the UK, the Middle East, Africa, and Southeast Asia often travel to India to undergo this vision-restoring procedure at a fraction of the cost they would pay in their home country.
- In the United States, a corneal transplant surgery can cost between $13,000 and $25,000, depending on the hospital, surgeon, and insurance coverage. The price often includes donor tissue, surgery, and post-op care—but with a high degree of variability and hidden fees.
- In the United Kingdom, the cost ranges between £8,000 to £12,000 (approximately $10,000 to $15,000), and it can take months to access donor tissue through the NHS. Private options are quicker but more expensive.
- In countries like Canada and Australia, the price generally falls between $8,000 - $13,000, and patients often face long wait times if going through public systems.
- In the UAE and Gulf region, private hospitals charge $6,000 to $10,000 for a corneal transplant, making it more affordable than in the West but still much costlier than in India.
In contrast, the cost of a corneal transplant in India ranges from just $600 to $2,900. It includes consultation, surgery, certified donor tissue, and initial post-operative care. Even for advanced types like DMEK or artificial cornea procedures, India’s pricing remains highly competitive.
|
Country |
Approximate Cost (USD) |
Savings in India (%) |
|
India |
$600 – $2,900 |
– |
|
United States |
$13,000 – $25,000 |
85% – 95% |
|
United Kingdom |
$10,000 – $15,000 |
80% – 90% |
|
Canada |
$9,000 – $13,000 |
80% – 88% |
|
Australia |
$8,000 – $12,000 |
78% – 86% |
|
UAE |
$6,000 – $10,000 |
70% – 82% |
What are the Factors Affecting Eye Transplant Cost in India?
The cost of a corneal transplant in India varies from one patient to another based on several important factors. Understanding these variables can help patients and their families make informed decisions and plan their treatment budgets effectively.
- Type of Corneal Transplant Performed: Different types of transplants have different complexities and associated costs. A Penetrating Keratoplasty (PK) is relatively less expensive, while DSEK, DMEK, or artificial corneal implants (KPro) require higher surgical skill, thinner tissue preparation, and advanced tools, making them more expensive.
- Hospital Infrastructure and Accreditation: Multi-speciality hospitals or JCI/NABH-accredited eye care centres may charge more due to superior infrastructure, better infection control, advanced diagnostic tools, and international safety protocols. On the other hand, smaller clinics or charitable hospitals may offer the surgery at subsidised rates.
- Surgeon’s Experience and Reputation: Top-tier corneal surgeons with international fellowships, extensive surgical experience, and high success rates often charge premium fees. Their expertise, however, usually translates to fewer complications, better visual outcomes, and lower chances of graft rejection or failure.
- Source and Quality of Donor Cornea: The eye bank used plays a key role in pricing. Corneas sourced from private or internationally affiliated eye banks with better screening and preservation techniques may cost more than those provided by government or charitable institutions. The quality, freshness, and matching of donor tissue can also affect cost and outcome.
- Length of Hospital Stay and Post-Op Support: Most corneal transplants are day-care procedures, but patients who require overnight hospitalisation, extended monitoring, or additional nursing care may incur higher costs. Also, complex cases with co-existing eye conditions may need extra support, raising the overall cost.
- Post-Operative Medications and Visual Aids: The cost of recovery isn’t limited to surgery alone. Ongoing medications, special eye drops, bandage contact lenses, and visual rehabilitation (if required) can add to the total expense, especially in the first few weeks after surgery.
- Location of the Hospital (City Tier): Hospitals in metro cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bangalore may charge more compared to those in Tier 2 or Tier 3 cities. However, metros often offer more experienced surgeons, better donor cornea availability, and international patient departments.
These factors, when combined, influence whether the final cost of corneal transplantation in India falls toward the lower or higher end of the ₹50,000–₹2,50,000 range. For international patients, understanding these nuances helps in choosing the right combination of quality, cost, and convenience.
Why Choose India for Eye Transplant (Corneal Transplant) Surgery?
India has become one of the world’s most trusted destinations for affordable, high-quality corneal transplant surgery. From advanced surgical techniques to internationally trained specialists and world-class infrastructure, patients across continents choose India for vision restoration with confidence.
- World-Class Eye Hospitals and Surgical Expertise: India is home to globally recognised eye hospitals such as Sankara Nethralaya, LV Prasad Eye Institute, Aravind Eye Hospital, and others, known for excellence in corneal care. These centres offer a wide range of transplant techniques—from Penetrating Keratoplasty to DMEK and Boston KPro—with high surgical success rates. Surgeons often have international training and fellowships in corneal and refractive surgery.
- Advanced Technology with FDA-Approved Procedures: Top centres in India use cutting-edge diagnostic tools such as anterior segment OCT, specular microscopy, and corneal topography to determine the best surgical approach. Techniques like lamellar transplants (DALK, DMEK) are performed routinely with precision equipment and sterile protocols matching Western standards.
- Affordable Pricing with No Compromise on Quality: While a corneal transplant abroad may cost over $10,000, in India, it is available for as low as $600. The savings of 70–90% are achieved without compromising on quality, as Indian hospitals follow evidence-based protocols, ethical tissue handling, and standardised care.
- Reliable Access to Donor Corneas: India has a robust network of certified eye banks, including government and private facilities, which ensures a steady supply of high-quality donor tissue. Waiting times are minimal, and international patients can undergo surgery within days of arrival.
International Patient Support for Eye Transplant in India
India’s leading eye hospitals offer dedicated services for international patients, ensuring a smooth and stress-free experience from pre-travel planning to post-surgery care. With growing numbers of patients travelling from countries like Nigeria, Kenya, UAE, Iraq, Bangladesh, and Sri Lanka, hospitals have built specialised departments that focus on end-to-end patient coordination and comfort.
- Visa Assistance and Medical Invitation Letters: Hospitals in India provide prompt support for medical visa documentation, including invitation letters that detail the purpose of travel, treatment plan, and hospital credentials. These are accepted by Indian embassies and consulates worldwide, helping patients secure visas faster.
- Airport Transfers and Local Transport: Most centres arrange complimentary or paid airport pickups, ensuring that patients are transported safely to their accommodation or directly to the hospital. Coordinators also assist with local transport for appointments and follow-ups.
- Help with Accommodation: Eye hospitals collaborate with partner hotels, guest houses, and service apartments near the facility. Patients and family members can choose from various pricing options, often with hospital-negotiated discounts and meal plans.
- Multilingual Interpretation and Translation: To overcome language barriers, hospitals provide interpreters or multilingual patient care managers fluent in Arabic, French, Swahili, Bengali, and other regional or international languages. It ensures effective communication with doctors and nurses throughout the treatment.
- Personalised Patient Coordination: Each international patient is assigned a dedicated coordinator who helps with scheduling consultations, pre-surgery tests, travel arrangements, and billing. They act as a 24/7 support point during your medical stay.
- Flexible Payment Options and Advance Booking: Hospitals accept multiple international payment methods, including bank transfers, credit cards (Visa, Mastercard), and some digital wallets. Many hospitals allow patients to pre-book surgeries and confirm donor tissue availability before arriving.
International patients undergoing corneal transplant surgery in India benefit from a system designed to be efficient, affordable, and compassionate, helping them focus on healing while the logistics are handled professionally.
Success Rate and Recovery Timeline for Eye Transplant in India
Undergoing a corneal transplant in India offers not only affordability but also high success rates and well-structured recovery protocols. Thanks to advancements in surgical techniques and donor screening, the graft survival and visual improvement rates are among the best in the world.
Success Rate of Corneal Transplant Surgery
The success of an eye transplant depends on the type of surgery performed, the underlying condition, and patient compliance. In India, the average success rate ranges between 85% and 95%, especially in well-matched cases with healthy donor tissue.
- For Penetrating Keratoplasty, the graft survival rate is typically 80–90% at 1 year, and about 60–75% at 5 years, depending on the cause.
- For DSEK or DMEK (endothelial transplants), success rates are even higher—up to 95% in uncomplicated cases, with better long-term outcomes and lower rejection risks.
- In complex or high-risk cases (e.g., multiple grafts, infections), outcomes vary but can still be favourable with careful follow-up.
India’s top eye surgeons use advanced tools and protocols to minimise rejection risk, enhance healing, and promote long-term graft clarity.
Recovery Timeline After Corneal Transplant
Recovery from a corneal transplant takes time and requires patience. Immediately after surgery, patients may experience blurry or hazy vision, mild irritation, and light sensitivity. It is normal and gradually improves over weeks to months.
- First week: Vision remains blurry. A protective eye shield is used, and drops are started to prevent infection and inflammation.
- 2–4 weeks: Gradual improvement in clarity. Most patients can resume light activities but must avoid rubbing the eye, bending forward, or lifting heavy objects.
- 1–3 months: Vision continues to improve. Stitches (if used) may be removed in stages, and refraction can be tested for corrective lenses.
- 6–12 months: Full visual potential is typically reached. Patients may need new glasses or contact lenses for optimal correction.
Close follow-up with the surgeon is essential to monitor for signs of graft rejection, elevated eye pressure, or infection. With proper care, the transplanted cornea remains clear and functional for many years.
Patient Testimonials – Eye Transplant Success Stories in India
“I came blind in one eye, and left seeing clearly again.”
Name: Zenb M.
Country: Kenya
Experience: “I had keratoconus for years, and my left eye had gone almost blind. The hospitals in Nairobi advised me to go abroad for a transplant. I found a corneal specialist in India who explained everything clearly. Within two weeks, I had my surgery and recovery began. Now I can see clearly again. The hospital team even helped my husband with a hotel stay and daily transport.”
“India gave me back my sight and my independence.”
Name: Sameer R.
Country: Iraq
Experience: “I suffered from a corneal infection that left a white scar in my eye. I couldn't drive, read, or work properly. I travelled to India, where doctors performed DSEK surgery with donor tissue. The results were life-changing. The staff spoke Arabic, and everything was well coordinated, from visa to surgery to my follow-up. I only wish I had done this earlier.”
“My son’s vision was saved thanks to India’s expert care.”
Name: Alia Z.
Country: UAE
Experience: “My 12-year-old son needed a corneal transplant after an injury. We were afraid of complications, but the pediatric ophthalmology team in India was outstanding. They had child-specific eye care and ensured we felt safe throughout. Today, my son is back in school, reading and playing again. Thank you, India!”
Frequently Asked Questions
No, a full eye (globe) transplant is not medically possible anywhere in the world due to the inability to reconnect the optic nerve. What’s commonly called an "eye transplant" is actually a corneal transplant, which replaces only the transparent front part of the eye.
Patients with conditions like keratoconus, corneal scarring, Fuchs’ dystrophy, corneal ulcers, or failed previous grafts are usually eligible, provided they have no active eye infection or uncontrolled systemic diseases.
No, the procedure is typically done under local anaesthesia or mild sedation. Patients may experience minor discomfort or irritation for a few days after surgery, but severe pain is uncommon.
Initial visual improvement begins in 1–2 weeks, but full visual recovery can take 3 to 6 months, depending on the type of surgery. Fine-tuning of vision with glasses or contact lenses is sometimes needed afterwards.
While the success rate is high, possible risks include graft rejection, infection, elevated eye pressure, or delayed healing. Regular follow-up and proper use of medications reduce these risks significantly.
A successful graft can last 10 years or longer. With proper care and regular monitoring, many patients enjoy stable vision for decades after the transplant.
The average cost of a corneal transplant in India ranges from ₹50,000 to ₹2,50,000, or approximately $600 to $2,900. The final price depends on the type of transplant, the hospital, and the source of donor tissue.
In most private hospitals, yes—the package includes certified donor tissue sourced from a licensed eye bank. Always confirm this when booking your surgery.
Yes, most hospitals in India accept international credit cards, wire transfers, and cash payments in foreign currencies. It’s advised to get a formal invoice in advance for visa and budgeting purposes.
Yes. Full-thickness PK is usually on the lower end of the cost range, while advanced procedures like DSEK or DMEK require specialised instruments and skills, raising the overall cost.