Eye Cancer Treatment Cost in India
When diagnosed with eye cancer, patients not only worry about their health but also face the overwhelming challenge of accessing high-quality, affordable treatment. For many, India has emerged as a leading destination for advanced eye cancer care, offering world-class medical expertise, state-of-the-art facilities, and significantly lower costs compared to Western countries.
Eye cancer, though relatively rare, can affect both children and adults and requires a highly specialized approach for diagnosis and treatment. Whether it's retinoblastoma in children, ocular melanoma in adults, or orbital lymphoma, Indian hospitals provide comprehensive care. It includes advanced imaging, surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and innovative treatments like plaque brachytherapy.
The cost of eye cancer treatment in India ranges from $2,500 to $10,000, depending on the type of cancer, stage of disease, treatment method, and hospital choice. It is up to 70–80% lower than what patients might pay in the United States, UK, UAE, or many parts of Africa, making India a globally preferred medical tourism hub for oncology care.
Table of Contents
What is Eye Cancer?
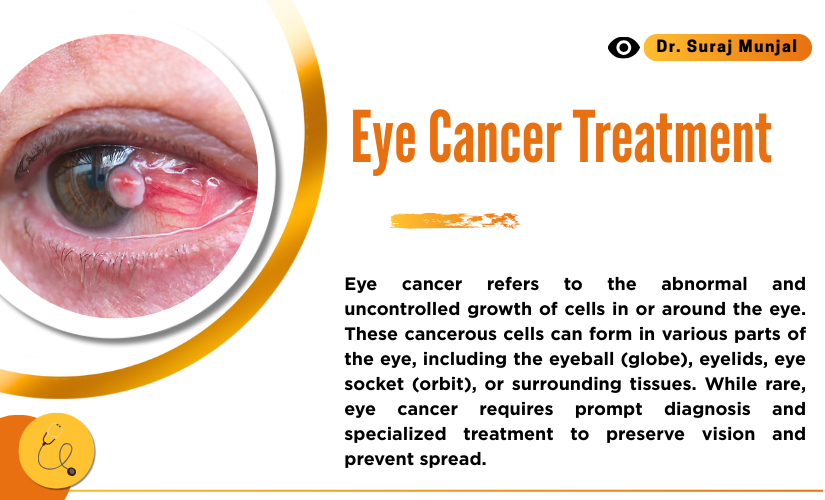
Eye cancer refers to the abnormal and uncontrolled growth of cells in or around the eye. These cancerous cells can form in various parts of the eye, including the eyeball (globe), eyelids, eye socket (orbit), or surrounding tissues. While rare, eye cancer requires prompt diagnosis and specialized treatment to preserve vision and prevent spread.
Doctors categorize eye cancer into two main groups: primary (originating in the eye) and secondary (spreading from another part of the body). Primary eye cancer is more commonly seen in children (e.g., retinoblastoma) and adults (e.g., ocular melanoma or lymphoma).
In most cases, eye cancer progresses silently in the early stages. Without effective treatment, the disease can cause serious complications such as vision loss, eye removal, or even metastasis to the brain or bones. Hence, early detection of eye cancer plays a crucial role in successful treatment outcomes.
Eye oncologists in India utilize advanced technologies and multidisciplinary approaches to effectively treat eye cancer. Whether the goal is to cure the cancer or preserve vision, patients receive customized care backed by global protocols.
What are the Most Common Types of Eye Cancer?
Eye cancer encompasses several distinct types, each with unique characteristics, specific age groups affected, and distinct treatment approaches. The most common eye cancers are:
- Retinoblastoma (Most Common in Children: Retinoblastoma is a rare but aggressive eye cancer that develops in the retina, primarily affecting children under the age of five. It often presents as a white reflection in the pupil, squint, or poor vision in one or both eyes. Retinoblastoma can be life-threatening if not treated early, but it has a high cure rate when detected in time. Indian hospitals offer specialized pediatric oncology units that treat retinoblastoma using a combination of chemotherapy, focal therapy (like laser or cryotherapy), and enucleation when needed.
- Uveal Melanoma (Most Common in Adults): Uveal melanoma arises from the pigmented cells in the uvea, the middle layer of the eye. It is the most frequent primary eye cancer in adults. Unlike skin melanoma, this form may not show symptoms until it affects vision or spreads to other organs. Treatment options in India include plaque brachytherapy, surgical removal, or radiation therapy, depending on tumor size and location.
- Conjunctival Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This type of eye cancer affects the conjunctiva, the thin, transparent tissue that covers the white of the eye. It may appear as a growing pink mass and is more common in regions with high UV exposure. Doctors often manage it with surgical excision, topical chemotherapy, or cryotherapy. In advanced cases, radiation or additional surgery may be necessary.
- Orbital Rhabdomyosarcoma: Typically seen in children and teenagers, rhabdomyosarcoma is a soft tissue cancer. It develops in the muscles surrounding the eye. It causes rapid swelling, eye displacement, and sometimes pain. Treatment usually involves chemotherapy and radiation, with surgery reserved for specific cases. Indian oncology centers offer protocols that follow global pediatric cancer treatment guidelines.
- Intraocular Lymphoma: Intraocular lymphoma typically affects elderly individuals and is often linked to central nervous system lymphoma. It may mimic uveitis (eye inflammation), which delays diagnosis. This cancer usually requires chemotherapy and targeted immunotherapy rather than surgery.
By identifying the specific type of eye cancer, Indian specialists tailor treatment plans to each patient's age, disease stage, and health condition. Their multidisciplinary approach ensures that patients receive both disease control and functional eye preservation when possible.
What are the Symptoms of Eye Cancer?
Eye cancer often develops silently, especially in the early stages. Many symptoms mimic common, non-cancerous eye conditions, which can delay diagnosis and treatment. Recognizing potential warning signs early gives patients a better chance of preserving both their vision and overall health.
The symptoms that require immediate medical evaluation by an ophthalmologist or eye oncologist are:
- Sudden or Gradual Vision Loss: A noticeable decline in vision—either central or peripheral—may indicate that a tumor is interfering with the retina, optic nerve, or other critical visual structures.
- White or Shiny Reflection in the Eye (Especially in Children): Parents may notice a white glow or reflection in the child's eye, often in flash photos. It is a classic sign of retinoblastoma and should be examined without delay.
- Bulging of the Eye (Proptosis): Protrusion or displacement of the eye can signal an orbital tumor, especially when it appears suddenly or is accompanied by swelling or discomfort.
- Dark Spot or Growth on the Eye Surface: A slowly growing pigmented or pink lesion on the conjunctiva or iris may indicate squamous cell carcinoma or melanoma. These lesions often go unnoticed until they affect appearance or function.
- Pain or Pressure in or Around the Eye: While pain is not always present in eye cancer, persistent discomfort or a feeling of fullness in the orbit should be evaluated, particularly if other signs accompany it.
- Redness or Persistent Irritation: Chronic redness or an inflamed appearance that doesn't respond to usual treatment could point to more serious conditions like lymphoma or conjunctival cancer.
- Sudden Onset of Floaters or Flashes: Floaters, flashes of light, or visual disturbances may indicate retinal involvement, which can be caused by tumors pressing on or within the eye's internal structures.
- Change in Eye Alignment or Squint: A sudden squint or crossed eye (strabismus), especially in young children, could be a sign of an intraocular tumor affecting eye movement or vision.
What are the Diagnostic Tests for Eye Cancer?
Accurate diagnosis plays a crucial role in the successful treatment of eye cancer. In India, hospitals utilize advanced diagnostic tools and protocols to detect diseases and determine their type and stage. These tests help ophthalmologists and oncologists assess the extent to which the cancer has progressed and whether it has spread beyond the eye.
- Comprehensive Eye Examination: Doctors begin with a detailed eye exam using slit-lamp biomicroscopy, indirect ophthalmoscopy, and pupillary dilation. These tests allow close inspection of the retina, optic nerve, and other internal eye structures. Any abnormal mass, bleeding, or unusual pigmentation raises suspicion for malignancy.
- Ocular Ultrasound (B-Scan Ultrasonography): It is a non-invasive test that utilizes sound waves to produce real-time images of the eye and its surrounding orbit. It helps detect tumors hidden behind the retina, determine tumor size, and assess involvement of the optic nerve. Ultrasound is especially valuable when the inside of the eye is obscured by hemorrhage or cataract.
- Fundus Photography and Fluorescein Angiography: Fundus photography captures HD images of the retina and optic disc. In fluorescein angiography, a contrast dye is injected into a vein, allowing doctors to study blood flow in the retina and choroid. These techniques help identify abnormal vessels, leakage, or hidden tumors.
- MRI and CT Scans: MRI provides detailed scans of soft tissues, making it ideal for examining intraocular and orbital tumors. CT scans are helpful in identifying calcifications (often seen in retinoblastoma) and assessing bone involvement. These scans also evaluate whether cancer has spread to surrounding areas or the brain.
- Biopsy and Fine Needle Aspiration Cytology (FNAC): In some cases, doctors may take a tissue or fluid sample to confirm the diagnosis. It is more common in orbital tumors, conjunctival cancers, or intraocular lymphomas. The sample undergoes pathological analysis to determine cell type and malignancy grade.
- Lumbar Puncture and Bone Marrow Tests (in retinoblastoma): When treating advanced retinoblastoma, doctors may perform a lumbar puncture and bone marrow biopsy to rule out metastasis to the central nervous system or bones. These tests help decide whether systemic chemotherapy is necessary.
- Genetic Testing: For hereditary eye cancers, such as bilateral retinoblastoma, genetic testing identifies mutations in the RB1 gene. It enables family screening and facilitates planning for long-term monitoring of at-risk siblings.
What are the Eye Cancer Treatment Options in India?
Eye cancer treatment depends on several factors, including the type of cancer, its size, location, and whether it has metastasized. In India, top hospitals use globally accepted treatment protocols tailored to each patient's condition. The goal is to eliminate the cancer, preserve vision whenever possible, and maintain the eye's structure and appearance.
- Chemotherapy: Doctors use chemotherapy to shrink or destroy cancer cells using potent anti-cancer drugs. Chemotherapy is often used in combination with focal therapy or surgery. It can be delivered in various forms:
- Intravenous (IV) Chemotherapy: Common for advanced or systemic disease, like retinoblastoma and lymphoma.
- Intra-arterial chemotherapy delivers drugs directly to the eye through the ophthalmic artery, thereby minimizing side effects. Often used in children with retinoblastoma.
- Intravitreal Chemotherapy: Injects medicine directly into the eye to treat recurrent or vitreous seeding cases.
- Radiation Therapy: Radiation uses high-energy rays to target and kill cancer cells. Two primary methods are used:
- External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT): Machines focus beams onto the tumor from outside the body. This method is effective, but it may also affect healthy tissues.
- Plaque Brachytherapy: A small radioactive disc is temporarily sewn onto the eye's surface near the tumor. This precise technique delivers high-dose radiation to the tumor with minimal damage to surrounding tissue. It's commonly used for uveal melanoma.
- Laser Therapy (Transpupillary Thermotherapy): Doctors use a focused infrared laser to generate heat and destroy small tumors, often in combination with chemotherapy. It's less invasive and helpful in treating small retinoblastomas and early-stage melanomas.
- Cryotherapy: It is a technique that uses extreme cold to freeze and destroy small, superficial tumors. Cryotherapy is frequently used alongside chemotherapy in early-stage retinoblastoma or conjunctival cancers.
- Surgical Removal (Enucleation or Exenteration): If the tumor is large or vision cannot be saved, doctors may surgically remove:
- The Eye (Enucleation): Recommended in advanced cases where preserving the eye is not feasible.
- The Eye and Surrounding Structures (Exenteration): Required for very aggressive tumors affecting the surrounding tissue. Surgeons later offer prosthetic eye fitting for cosmetic restoration.
- Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy: For cancers like intraocular lymphoma or metastatic disease, doctors may use immune checkpoint inhibitors or targeted agents. These therapies enhance the body's immune system to attack cancer cells or block specific pathways of cell growth.
- Observation and Monitoring: In some slow-growing tumors (e.g., small uveal melanoma or choroidal nevus), doctors may choose a watchful waiting approach with regular imaging and follow-up to monitor any changes.
What is the Cost of Eye Cancer Treatment in India?
India offers one of the most cost-effective yet high-quality options for eye cancer treatment worldwide. Whether it's pediatric retinoblastoma, adult ocular melanoma, or orbital tumors, Indian hospitals provide extensive care at a fraction of the fee charged in countries like the US, UK, UAE, or South Africa. The cost of eye cancer treatment in India ranges from $2,500 to $10,000, depending on several key factors:
- Type of cancer (e.g., retinoblastoma vs. uveal melanoma)
- Stage at diagnosis
- Mode of treatment (surgery, radiation, chemotherapy, or a combination)
- Duration of treatment and hospital stay
- Patient's age and general health
- Need for specialized equipment (e.g., plaque brachytherapy)
|
Treatment Type |
Approximate Cost (USD) |
|
Chemotherapy (per cycle) |
$500 – $800 |
|
Intra-arterial chemotherapy |
$2,500 – $4,000 |
|
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) |
$2,000 – $3,500 |
|
Plaque Brachytherapy |
$3,000 – $5,500 |
|
Enucleation (eye removal surgery) |
$1,800 – $2,500 |
|
Prosthetic Eye Fitting |
$500 – $1,000 |
|
Cryotherapy / Laser Therapy |
$800 – $1,200 |
|
Immunotherapy / Targeted Therapy (if used) |
Varies widely ($3,000+) |
These are indicative prices and may vary slightly depending on the hospital, city, and patient needs. Unlike Western countries, where each element (surgeon fee, anesthetist fee, scans, hospitalization) is billed separately, Indian hospitals often offer bundled packages that make the total cost more transparent and affordable.
Patients also benefit from significantly lower medication and diagnostic imaging costs, further reducing the financial burden of long-term cancer care.
What are the Factors That Affect the Cost of Eye Cancer Treatment?
The cost of eye cancer treatment can vary significantly from one patient to another. Several key factors influence overall expenditure, and understanding these factors can help patients with eye cancer make informed decisions when planning their care.
- Type and Stage of Cancer: Advanced cancers often require more aggressive and prolonged treatment, such as multiple chemotherapy cycles, radiation, or enucleation. In contrast, early-stage cancers can usually be managed with localized therapies, such as laser or cryotherapy, thereby reducing total costs.
- Age and General Health of the Patient: Children, especially those with retinoblastoma, may need pediatric oncology care, general anesthesia for every procedure, and long-term monitoring, increasing the cost. Elderly or high-risk patients may also require additional medical support or ICU care.
- Choice of Treatment Modalities: Treatments such as plaque brachytherapy, intra-arterial chemotherapy, or immunotherapy are more advanced and costly than standard external beam radiation or conventional chemotherapy. When multiple therapies are combined, the overall cost rises accordingly.
- Hospital Infrastructure and Location: Premier hospitals in metro cities like Delhi, Mumbai, and Bangalore may charge slightly more than regional centers due to superior infrastructure, international accreditations, and access to cutting-edge technology. However, even the highest-end Indian hospitals remain affordable compared to global pricing.
- Surgeon's Experience and Specialization: Highly skilled ocular oncologists with global exposure or training may command higher fees. Choosing an experienced surgeon ensures better outcomes, especially for vision-sparing techniques.
- Diagnostic and Pre-treatment Workups: A comprehensive diagnosis may include imaging tests (such as MRI and ultrasound), blood tests, genetic testing, and biopsies. The number and complexity of these tests will affect upfront expenses.
- Duration of Hospital Stay and Postoperative Care: More complex surgeries, such as exenteration or procedures involving implants, may require extended recovery and hospitalization, which can impact the final cost. Some patients may also need physiotherapy or prosthetic fitting afterward.
Cost Comparison: India vs USA, UK, UAE, and Africa
One of the many reasons global patients choose India for eye cancer treatment is the remarkable cost difference, without compromising on quality. Indian hospitals offer world-class care at a fraction of the cost that patients typically pay in developed countries. This affordability, combined with advanced infrastructure and experienced specialists, makes India a global leader in eye oncology.
|
Country |
Approximate Cost Range (USD) |
|
India |
$2,500 – $10,000 |
|
United States |
$25,000 – $75,000+ |
|
United Kingdom |
$20,000 – $60,000 |
|
UAE |
$15,000 – $40,000 |
|
South Africa |
$10,000 – $30,000 |
|
Nigeria/Kenya |
$8,000 – $20,000 (limited availability) |
Note: These figures reflect a combination of surgery, chemotherapy, radiation, diagnostics, and hospital stays. Prices may vary depending on the type of hospital, insurance coverage, and the complexity of the cancer.
This price advantage has made India a preferred destination, particularly for patients from the GCC region (Oman, Qatar, Kuwait, and Bahrain), African nations (Nigeria, Kenya, Ghana, and Ethiopia), and Southeast Asia.
Success Rates and Treatment Outcomes
India has earned global recognition for its high success rates in treating eye cancer. Thanks to early diagnosis, specialized oncology teams, and access to advanced technologies, patients have excellent chances of recovery and vision preservation when treated in time.
Success Rates by Type of Eye Cancer
- Retinoblastoma: When diagnosed early, India achieves a survival rate of over 95%, comparable to top international centers. Many children retain full or partial vision, particularly with eye-sparing therapies like intra-arterial chemotherapy and focal laser treatments.
- Uveal Melanoma: Indian hospitals report a local control rate of 85–90% for medium-sized tumors treated with plaque brachytherapy or radiation. Enucleation, when necessary, achieves complete tumor removal and prevents metastasis in most cases.
- Conjunctival Tumors: For early-stage squamous cell carcinoma and melanoma of the conjunctiva, cure rates exceed 90% with surgical excision and adjunctive therapies.
- Orbital and Intraocular Lymphomas: When treated with systemic chemotherapy or radiotherapy, patients experience high response rates and disease control, especially in localized stages.
Key Factors That Influence Outcomes
- Early detection significantly improves both survival and vision preservation.
- Type and stage of cancer play a significant role; aggressive or metastatic tumors may require prolonged or multimodal treatment.
- The expertise of the oncology team in balancing tumor control with vision-saving techniques is crucial.
- Post-treatment monitoring ensures recurrence is caught early and managed promptly.
Visual and Cosmetic Outcomes
Preserving vision and appearance is often possible, especially in early cases. For patients requiring enucleation or exenteration, Indian hospitals offer high-quality ocular prostheses that provide excellent cosmetic results and enhance quality of life.
Services for International Patients
India has become a preferred destination for eye cancer treatment, not only because of its affordability but also due to the comprehensive care offered to international patients. Hospitals provide structured support systems to make the medical journey smooth, stress-free, and efficient.
The key services international patients receive during their treatment journey are:
- Dedicated international patient coordinators provide assistance with everything from medical inquiries to travel arrangements, hospital appointments, and billing support.
- Visa assistance is provided through official invitation letters issued by hospitals to help patients and caregivers secure medical visas without delay.
- Most hospitals or medical facilitators arrange airport pick-up and drop-off services to ensure a safe and convenient arrival and departure.
- Language interpretation support is available for Arabic, French, Swahili, and many other African and Southeast Asian languages, helping patients communicate comfortably with doctors and staff.
- Customized treatment packages are offered based on the patient's condition, along with itemized cost estimates, allowing patients to plan their budget before travel.
- In-hospital accommodation for attendants is available in many centers, especially those treating pediatric cases, allowing family members to stay close to their loved ones.
- Assistance with currency exchange, local SIM, and banking is often provided by hospital helpdesks for the convenience of international visitors.
- Prosthetic eye fitting and counseling are arranged for patients undergoing enucleation, ensuring cosmetic restoration and emotional support post-surgery.
- Teleconsultation services, available before arrival and after discharge, enable patients to connect with specialists to understand their options or follow up on their recovery from the comfort of their home country.
Patient Testimonials
Amina Yusuf – Jordan
"My 3-year-old daughter was diagnosed with retinoblastoma, and we were terrified. After researching several countries, we chose India for its advanced treatment options. At a leading cancer center in Delhi, the doctors started intra-arterial chemotherapy immediately. Within a few months, her tumor shrank significantly, and her eye was saved. The care, affordability, and kindness we received were beyond expectations."
Salem Al-Naimi – Oman
"I was diagnosed with uveal melanoma and advised to undergo plaque brachytherapy. The cost of treatment in my country was overwhelming, so I flew to India. The team was professional and reassuring throughout. My tumor was treated successfully, and I still have usable vision in my affected eye. I'm grateful to the medical staff for their expertise and support."
Miriam Otieno – Kenya
"When my elderly mother began to lose vision rapidly, we discovered she had intraocular lymphoma. We traveled to India, where she underwent a series of chemotherapy cycles. Her response has been excellent, and her condition is now under control. The hospital also provided interpreter support and assisted us in managing our accommodations. I recommend this place to anyone looking for affordable cancer care."
Frequently Asked Questions
Yes, many types of eye cancer are curable, especially when diagnosed early. For example, retinoblastoma in children has a survival rate above 95% with timely treatment. Localized tumors like conjunctival melanoma or uveal melanoma also respond well to surgery, laser therapy, or radiation.
The average cost of eye cancer treatment in India ranges between $2,500 and $10,000, depending on the type of cancer, treatment protocol, hospital, and duration of care.
For focal therapies or brachytherapy, a stay of 1–2 weeks may be sufficient. Patients requiring chemotherapy cycles or surgery followed by radiation may need to stay for 4–6 weeks or return for follow-up visits.
Not always. Many patients retain good vision if the cancer is detected early and treated with eye-conserving therapies. In some cases, especially with large tumors or aggressive cancers, surgery may be necessary, but options like prosthetic eyes ensure cosmetic restoration.
Yes. Most leading hospitals in India offer priority appointments, fast-track diagnostics, and dedicated international patient coordinators. There are usually no waiting lists, and treatment can begin as soon as diagnosis is confirmed.
Some Indian hospitals accept international insurance, but it is advisable to verify with your insurer in advance. Patients without insurance often benefit from transparent, bundled pricing that makes out-of-pocket expenses more manageable.
India has several specialized pediatric oncology units that offer child-friendly environments, anesthesia-assisted procedures, and genetic counseling. These centers also provide family accommodation and long-term follow-up for developmental support.